A(n) _____ is made from killed bacteria or damaged particles from bacterial cell walls or viruses. Its purpose is to prevent some diseases.
- antibiotic
- flagella
- anaerobe
- vaccine
_____ are long, thin whiplike structures that help organisms move.
- Endospores
- Flagella
- Nodules
- Bacilli
A(n) _____ is an organism that uses oxygen for respiration.
- anaerobe
- endospore
- aerobe
- saprophyte
A(n) _____ is an organism that lives without oxygen.
- anaerobe
- endospore
- aerobe
- saprophyte
A _____ is a plant that obtains nutrition from dead and decaying plant or animal tissue
- saprophyte
- pathogen
- cocci
- spirilla
_____ is the chemical transformation of nitrogen from the atmosphere into forms available to plants for growth.
- Nitrogen-fixation
- Fission
- Cyanobacteria
- Vaccination
A(n) _____ is a bacterium or virus that causes disease.
- vaccine
- saprophyte
- antibiotic
- pathogen
_____ inhibit the growth of or destroy bacteria.
- Vaccines
- Bacilli
- Pathogens
- Antibiotics
A(n) _____ is a poison produced by certain animals, plants, or bacteria.
- pathogen
- toxin
- endospore
- cocci
The heat-resistant structure in bacteria is the _____.
- saprophyte
- flagella
- anaerobe
- endospore
_____ are sphere-shaped bacteria.
- Bacilli
- Cocci
- Flagella
- Nodules
_____ is a form of asexual bacterial reproduction.
- Conjugation
- Fission
- Thermodynamics
- Intersection
_____ are bacteria shaped like rods.
- Cocci
- Flagella
- Pathogens
- Bacilli
Growths on roots of pea plants where good bacteria live are _____.
- nodules
- bacilli
- cocci
- flagella
The globular groups containing many cyanobacteria are referred to as _____.
- colonies
- bacilli
- cocci
- niches
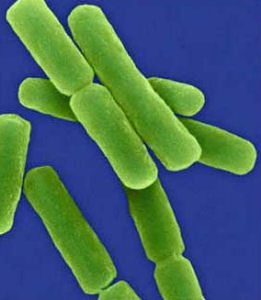
Below is a picture of the E. coli bacteria. It is a type of _____ bacteria.

- bacilli
- cocci
- spirilla
- Hot Tamale
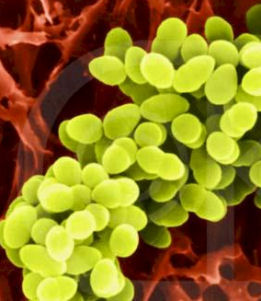
Below is a picture of bacteria. It is a type of _____ bacteria.
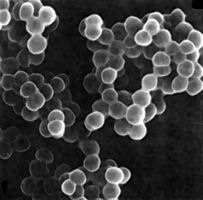
- bacilli
- cocci
- spirilla
- raspberry
Below is a picture of bacteria. It is a type of _____ bacteria.
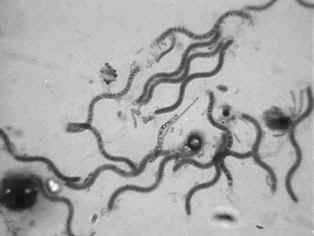
- bacilli
- cocci
- spirilla
- macaroni
Making medicines is a helpful use of _____.
- other eubacteria
- cyanobacteria
- nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Food for fish is a helpful use of _____.
- other eubacteria
- cyanobacteria
- nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Producing cheese is a helpful use of _____.
- other eubacteria
- cyanobacteria
- nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Decomposing other materials is a helpful use of _____.
- other eubacteria
- cyanobacteria
- nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Fertilizer is a helpful use of _____.
- other eubacteria
- cyanobacteria
- nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Cleaning up oil spills is a helpful use of _____.
- other eubacteria
- cyanobacteria
- nitrogen-fixing bacteria
Botulism is _____.
- food poisoning
- a bacteria that helps decompose other materials
- a type of viral infection
- a bacteria-eating organism
Botulism is caused by _____.
- viruses
- antibiotics
- bacteria
- vaccines
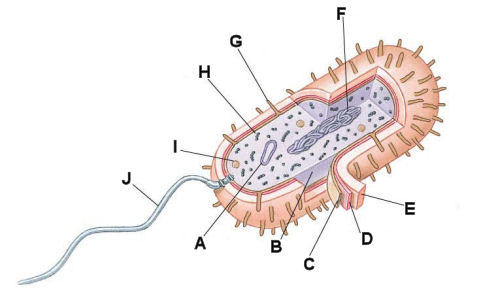
The letter "A" in the diagram below is the _____.
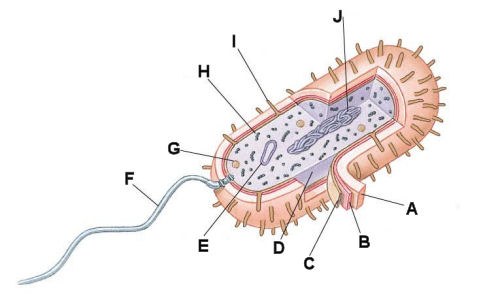
- cell membrane
- gelatinlike capsule
- cell wall
- cytoplasm
The letter "A" in the diagram below is the _____.
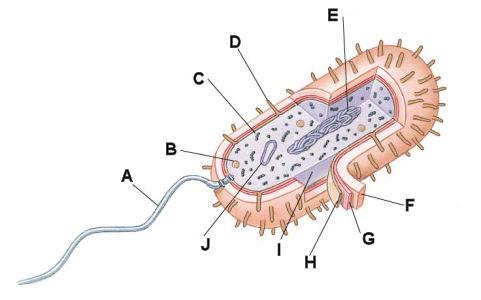
- flagellum
- chromosome
- ribosome
- cytoplasm
The letter "B" in the diagram below is the _____.
- cell wall
- cell membrane
- gelatinlike capsule
- cytoplasm
The letter "B" in the diagram below is the _____.

- cell membrane
- cell wall
- gelatinlike capsule
- cytoplasm
The letter "C" in the diagram below is the _____.

- cell membrane
- cytoplasm
- ribosome
- cell wall
The letter "C" in the diagram below is the _____.

- ribosome
- cytoplasm
- flagellum
- chromosome
The letter "C" in the diagram below is the _____.

- gelatinlike capsule
- cytoplasm
- cell wall
- cell membrane
The letter "D" in the diagram below is the _____.

- cell membrane
- cell wall
- gelatinlike capsule
- flagellum
The letter "D" in the diagram below is the _____.

- cell membrane
- cell wall
- cytoplasm
- gelatinlike capsule
The letter "E" in the diagram below is the _____.

- gelatinlike capsule
- cell wall
- cell membrane
- ribsome
The letter "E" in the diagram below is the _____.

- ribosome
- cytoplasm
- flagellum
- chromosome
The letter "F" in the diagram below is the _____.

- chromosome
- flagellum
- cytoplasm
- ribosome
The letter "F" in the diagram below is the _____.

- gelatinlike capsule
- cell wall
- cell membrane
- candy-coated shell
The letter "F" in the diagram below is the _____.

- flagellum
- ribosome
- cytoplasm
- chromosome
The letter "G" in the diagram below is the _____.

- cell membrane
- cell wall
- cytoplasm
- flagellum
The letter "H" in the diagram below is the _____.

- cytoplasm
- cell wall
- cell membrane
- gelatinlike capsule
The letter "H" in the diagram below is the _____.

- cytoplasm
- flagellum
- chromosome
- ribosome
The letter "H" in the diagram below is the _____.

- cytoplasm
- chromosome
- ribosome
- flagellum
The letter "I" in the diagram below is the _____.

- cytoplasm
- cell wall
- gelatinlike capsule
- cell membrane
The letter "J" in the diagram below is the _____.

- inclusion
- plasmid
- pilus
- flagellum
The letter "J" in the diagram below is the _____.

- chromosome
- plasmid
- ribosome
- cytoplasm
The cell shape in the picture below is _____.
- flagellum
- spirillum
- coccus
- bacillus
The cell shape in the picture below is _____.
- flagellum
- spirillum
- coccus
- bacillus
The cell shape in the picture below is _____.

- flagellum
- spirillum
- coccus
- bacillus
Cocci bacteria are ____-shaped.
- sphere
- spiral
- rod
- triangular
Spirilla bacteria are ____-shaped.
- sphere
- rod
- spiral
- octangular
Bacilli bacteria are ____-shaped.
- sphere
- rod
- spiral
- rectangular
The difference between aerobic and anaerobic bacteria is aerobic use _____ and anaerobic do not.
- flagella
- fission
- oxygen
- ribosomes
The two kingdoms of bacteria are _____.
- cyanobacteria and magnabacteria
- eucalyptic and archaeic
- eubacteria ad archaebacteria
- anaerobic and aerobic
Most bacteria reproduce through _____.
- fission
- mutation
- cloning
- conjugation
Bacteria live in groups called _____ which are usually circular.
- flagella
- kingdoms
- niches
- colonies
_____ are organisms that use dead organisms as a food source and help recycle nutrients so they are available for use by other organisms.
- Sessiles
- Saprophytes
- Setae
- Sporophytes
Chemicals produced by some bacteria that are used to limit the growth of other bacteria are _____.
- antibiotics
- antibodies
- antigens
- algae
_____ are poisons produced by pathogens.
- Sporangium
- Bacteria
- Toxins
- Lymphocytes
_____ bacteria save farmers millions of dollars every year in fertilizer costs.
- Anaerobic
- Nitrogen-fixing
- Endosporic
- Pathogenic
_____ can fight some bacterial diseases.
- Antibiotics
- Viruses
- Pathogens
- Toxins
The process of heating food to a temperature that kills most harmful bacteria without much effect on its taste is _____.
- conjugation
- fission
- nitrogen-fixing
- pasteurization
A(n) _____ uses oxygen to break down food to obtain energy.
- eubacterium
- anaerobe
- aerobe
- producer
A _____ is an organism that makes its own food using energy from the Sun.
- producer
- consumer
- pathogen
- plasmid
_____ help bacteria move around in moist areas.
- Cytoplasm
- Plasmids
- Ribosomes
- Flagella
Single-celled prokaryotic organisms that occur alone, in chains, or groups are _____.
- bacteria
- chromosomes
- ribosomes
- flagella
The kingdom of bacteria that lives in extreme environments is _____.
- archaebacteria
- eubacteria
- arteriobacteria
- antibacteria
_____ is a type of asexual reproduction in which two identical bacteria cells are produced from the original cell.
- Conjugation
- Fission
- Mutation
- Conjunction
_____ was the Dutchman who used a microscope to discover bacteria.
- Van Leeuwenhoek
- Pasteur
- Bacilli
- Von Bacitracin
An organism that breaks down and uses other organisms for energy is a _____.
- consumer
- producer
- anaerobe
- archaebacteria
During _____ bacteria exchange genetic material through sexual reproduction.
- mutation
- fusion
- fission
- conjugation
The largest bacteria kingdom which is classified into small groups by shape, structure, method of obtaining food, and their waste is _____.
- eubacteria
- archaebacteria
- aerobacteria
- anaerobacteria
The part of the bacterial cell which contains heredity material, and is the location of most of a cell's life processes is the _____.
- cytoplasm
- flagella
- capsule
- plasmid
_____ are the small cytoplasmic structures on which cells make their own protein.
- Plasmids
- Ribosomes
- Chromosomes
- Protists
A small circular piece of DNA is a _____.
- plasmid
- chromosome
- ribosome
- cocci
The _____ encloses, supports, and protects the cells of plants, algae, fungi, and most bacteria.
- cell wall
- cell membrane
- capsule
- cytoplasm
The _____ is the protective outer covering that regulates interaction between the cell and the environment.
- cell wall
- cell membrane
- capsule
- cytoplasm
The _____ protects bacterium from other cells that try to destroy them.
- cell wall
- cell membrane
- capsule
- cytoplasm
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek discovered bacteria in the _____ century.
- 16th
- 17th
- 18th
- 20th


























